Diabetes reversed in mice with genetically edited stem cells derived from patients
CRISPR corrects genetic defect so cells can normalize blood sugar
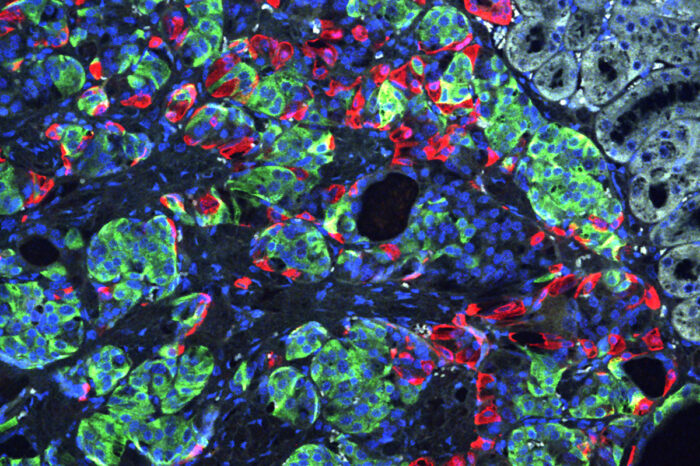 Millman lab
Millman labResearchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have transformed stem cells into insulin-producing cells. They used the CRISPR gene-editing tool to correct a defect that caused a form of diabetes, and implanted the cells into mice to reverse diabetes in the animals. Shown is a microscopic image of insulin-secreting beta cells (insulin is green) that were made from stem cells produced from the skin of a patient with Wolfram syndrome.
Using induced pluripotent stem cells produced from the skin of a patient with a rare, genetic form of insulin-dependent diabetes called Wolfram syndrome, researchers transformed the human stem cells into insulin-producing cells and used the gene-editing tool CRISPR-Cas9 to correct a genetic defect that had caused the syndrome. They then implanted the cells into lab mice and cured the unrelenting diabetes in those mice.
The findings, from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, suggest the CRISPR-Cas9 technique may hold promise as a treatment for diabetes, particularly the forms caused by a single gene mutation, and it also may be useful one day in some patients with the more common forms of diabetes, such as type 1 and type 2.
The study is published online April 22 in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
Patients with Wolfram syndrome develop diabetes during childhood or adolescence and quickly require insulin-replacement therapy, requiring insulin injections multiple times each day. Most go on to develop problems with vision and balance, as well as other issues, and in many patients, the syndrome contributes to an early death.
“This is the first time CRISPR has been used to fix a patient’s diabetes-causing genetic defect and successfully reverse diabetes,” said co-senior investigator Jeffrey R. Millman, PhD, an assistant professor of medicine and of biomedical engineering at Washington University. “For this study, we used cells from a patient with Wolfram syndrome because, conceptually, we knew it would be easier to correct a defect caused by a single gene. But we see this as a stepping stone toward applying gene therapy to a broader population of patients with diabetes.”
Wolfram syndrome is caused by mutations to a single gene, providing the researchers an opportunity to determine whether combining stem cell technology with CRISPR to correct the genetic error also might correct the diabetes caused by the mutation.
A few years ago, Millman and his colleagues discovered how to convert human stem cells into pancreatic beta cells. When such cells encounter blood sugar, they secrete insulin. Recently, those same researchers developed a new technique to more efficiently convert human stem cells into beta cells that are considerably better at controlling blood sugar.
In this study, they took the additional steps of deriving these cells from patients and using the CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing tool on those cells to correct a mutation to the gene that causes Wolfram syndrome (WFS1). Then, the researchers compared the gene-edited cells to insulin-secreting beta cells from the same batch of stem cells that had not undergone editing with CRISPR.
In the test tube and in mice with a severe form of diabetes, the newly grown beta cells that were edited with CRISPR more efficiently secreted insulin in response to glucose. Diabetes disappeared quickly in mice with the CRISPR-edited cells implanted beneath the skin, and the animals’ blood sugar levels remained in normal range for the entire six months they were monitored. Animals receiving unedited beta cells remained diabetic. Their newly implanted beta cells could produce insulin, just not enough to reverse their diabetes.
“We basically were able to use these cells to cure the problem, making normal beta cells by correcting this mutation,” said co-senior investigator Fumihiko Urano, MD, PhD, the Samuel E. Schechter Professor of Medicine and a professor of pathology and immunology. “It’s a proof of concept demonstrating that correcting gene defects that cause or contribute to diabetes — in this case, in the Wolfram syndrome gene — we can make beta cells that more effectively control blood sugar. It’s also possible that by correcting the genetic defects in these cells, we may correct other problems Wolfram syndrome patients experience, such as visual impairment and neurodegeneration.”
In the future, using CRISPR to correct certain mutations in beta cells may help patients whose diabetes is the result of multiple genetic and environmental factors, such as type 1, caused by an autoimmune process that destroys beta cells, and type 2, which is closely linked to obesity and a systemic process called insulin resistance.
“We’re excited about the fact that we were able to combine these two technologies — growing beta cells from induced pluripotent stem cells and using CRISPR to correct genetic defects,” Millman said. “In fact, we found that corrected beta cells were indistinguishable from beta cells made from the stem cells of healthy people without diabetes.”
Moving forward, the process of making beta cells from stem cells should get easier, the researchers said. For example, the scientists have developed less intrusive methods, making induced pluripotent stem cells from blood — and they are working on developing stem cells from urine samples.
“In the future,” Urano said, “we may be able to take a few milliliters of urine from a patient, make stem cells that we then can grow into beta cells, correct mutations in those cells with CRISPR, transplant them back into the patient, and cure their diabetes in our clinic. Genetic testing in patients with diabetes will guide us to identify genes that should be corrected, which will lead to a personalized regenerative gene therapy.”







