Mice with genetic defect for human stuttering offer new insight into speech disorder
Animal model may help scientists understand molecular, neurological basis of stuttering
 Robert Boston
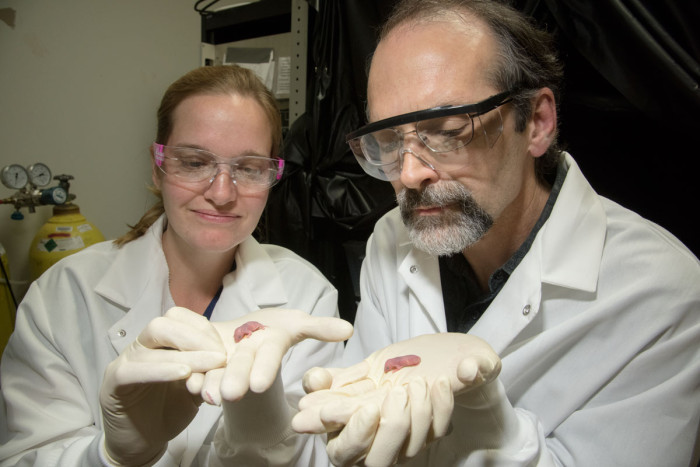
Robert BostonSenior scientist Terra Barnes, PhD, and Tim Holy, associate professor of neuroscience, PhD, hold mouse pups. Barnes and Holy recorded the vocalizations of 3- to 8-day-old mouse pups and found that those that carry a mutation in a gene associated with stuttering in humans produced abnormal vocalizations with pauses and repetitions similar to human stuttering.

Mice that vocalize in a repetitive, halting pattern similar to human stuttering may provide insight into a condition that has perplexed scientists for centuries, according to a new study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
The researchers created mice with a mutation in a gene associated with stuttering in humans and found that they vocalized in an abnormal pattern reminiscent of human stuttering. The animal model of stuttering can help scientists understand the molecular and neurological basis of the disorder, and potentially develop treatments.
The research is published online April 14 in Current Biology.
Once thought to be caused by nervousness, stress or even bad parenting, stuttering is now recognized as primarily biological in origin, although anxiety can exacerbate the condition.
Some people who stutter have a mutation in a gene called Gnptab (for N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase alpha and beta). With Dennis Drayna, PhD, and colleagues at the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, the researchers created mice with a corresponding mutation in the same gene and studied their vocalizations for evidence of abnormalities similar to human stuttering.
“Speech is obviously a unique human capacity, but the patterns of speech are built out of a lot of building blocks that are much simpler,” said Tim Holy, PhD, an associate professor of neuroscience and the paper’s senior author. “You have to be able to control the timing of your breath and the fine muscles in your tongue and mouth. You have to be able to initiate movement. Those kinds of things may be shared all the way from mice to people.”
Mice make complex sounds all the time, at pitches too high for the human ear to detect.
“Pups spontaneously vocalize when they are taken from their mom,” said first author Terra Barnes, PhD, a senior scientist in Holy’s lab. “Mice vocalize when they’re in pain, when they meet another mouse or to attract a mate.”
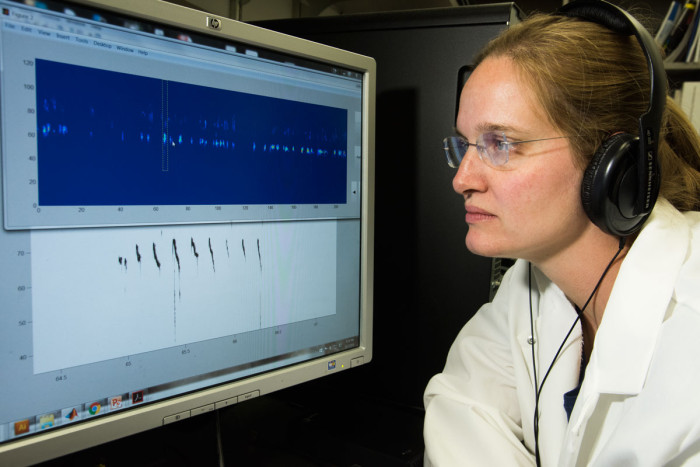
A key characteristic of stuttering is the presence of hesitations that break up the smooth flow of speech. Barnes and colleagues developed an algorithm to analyze the length of pauses in the spontaneous vocalizations of 3- to 8-day-old mouse pups. They found that mice carrying the mutation exhibited longer pauses than those without the mutation.
The researchers applied the same algorithm to recordings of people talking, some of whom stuttered and some of whom did not. The algorithm accurately distinguished people who speak fluently from people who stutter.
The scientists also found that the syllables vocalized by mice with the mutation were less random than those of mice without the mutation. In other words, similar to people who stutter, the mice with the mutation repeated the same syllables more often.
“We found abnormalities that mimic some features of human stuttering,” said Barnes.
Other than in their vocalizations, the mice with the mutation were normal. Co-author David Wozniak, PhD, professor of psychiatry at Washington University, and colleagues put the mice through a battery of tests — to check their balance, strength, coordination, movement initiation, spatial learning, memory, sociability and more — and found no substantial differences between mice with and without the mutation. In this respect, the mice with the mutation are like people who stutter — indistinguishable from nonstutterers in all but speech.
“One of the things we find scientifically interesting about stuttering is that it is so precisely limited to speech,” said Holy. “It’s a very clean defect in an incredibly complex task.”
It is not clear how the gene relates to speech. It is known to be involved in the pathway that degrades molecules inside the cell. Mutations that cause total loss of function result in serious metabolic diseases called mucolipidosis II/III, but the mutations associated with stuttering appear to preserve much of the known function of these genes.
“It’s kind of crazy that this gene that’s involved in digesting the garbage in your cells is somehow linked to something so specific as stuttering,” said Holy. “It could be that the protein has many functions and this mutation affects only one of them. Or the mutation could very mildly compromise the function of the protein, but there’s a set of cells in the brain that is exquisitely sensitive, and if you ever so slightly compromise the function in those cells you get the observable behavioral deficit.”
Now that researchers have a mouse model of stuttering, they are developing ideas to explore the disorder further. “We’re coming up with lots of studies we can do to figure this out,” said Barnes.
 Robert Boston
Robert Boston